Glucosamine is a substance often used by physically active individuals, who use it for the sole purpose of arthritis prevention.
If you are a beginner trainee and often rely on intense workout, which are extremely heavy for the joints and connective tissues, then keep reading to find out how this supplement will help you take care of your joints.
What Is Glucosamine?
Glucosamine is an amino-monosaccharide, which is often seen in chitin, hyaluronic acid and heparan sulfate.
In the shape of N-acetyl-glucosamine, it is in the content of more complex carbohydrates like glycoproteins, which are a basic building unit of connective tissues.
Glucosamine is the building block of creatine and hyaluronic acid.
It is a natural substance for the human body and it is most concentrated in the cartilages and joints.
Even though it is harder to do, glucosamine can be derived from food, as the richest sources are animal products.
Glucosamine can also be found in sea food- Mainly found in the shells of crustaceans.
Other highly concentrated sources of it are animal bones and when it comes to non-animal sources, mushrooms like Aspergillus Niger come in to play.
Types Of Glucosamine
There are two main types of glucosamine on the market- Sulfate and hydrochloride.
Glucosamine sulfate can be derived in a laboratory, through saccharides and glutamine, or even natural sources like sea shells, which we mentioned is a highly concentrated source.
It is worth mentioning that people allergic to sea food should avoid forms of the supplement, derived from such shells.
Glucosamine hydrochloride is an alternative version of glucosamine sulfate.
However, the chemically derived glucosamine hydrochloride has worse parameters in terms of digestibility and concentration in the tissues, compared to the glucosamine sulfate.
In recent years, plant glucosamine, which is practically glucosamine hydrochloride but naturally produced, has become viral on the market. The main source of plant glucosamine is the Aspergillus niger fungus, which is popular with its content of anti-inflammatory proteolytic enzymes.
Some studies have shown certain benefits of using glucosamine in the treatment of osteoarthritis and pain suppression, but more in-depth analyzes are needed.
This alternative vegetable glucosamine is a great choice for seafood allergy recipients who are prevented from using glucosamine sulfate therapy.
How Is Glucosamine Metabolized In The Organism?
It is absorbed in the small intestine and then transferred to the liver and joints.
A 2001 study in Italy shows that, after receiving 314 mg of crystalline glucosamine sulfate, marked and followed by ion-exchange chromatography, blood count and fecal mass analysis, its digestibility is not less than 88.7% of the initial dose.
Scientists have concluded that high absorption is due to the presence of bifidobacteria that accelerate the metabolism of glucosamine in the small intestine.
The glucosamine sulfate and glucosamine hydrochloride formulations are considered to have higher absorption, with the highest values of glucosamine sulfate reaching at least 88% absorption. Compared to this, pure glucosamine is digested up to 26%. In addition, glucosamine sulfate has a longer half-life and higher concentrations in the tissues and circulating levels.
Basic Physiological Effect Of Glucosamine
As we mentioned, the substance is used to slow down the damage caused by arthritis, but it can help physically active individuals with joint pains.
What Are The Optimal Doses?
Recommended daily glucosamine dosages range from 300 to 500 mg, split into 3 times during the day- This way, glucosamine is completely safe for the health.
A part of the positive effects of glucosamine depend on the dose, as in some researches, daily doses of up to 3000 mg are used, which, needless to say is not recommended without medical assurance.
It is usually recommended to take glucosamine in with food, as it is known to have stomach irritating properties.
Possible Side Effects Of Glucosamine
It is possible for some people to be allergic to glucosamine.
This allergic reaction is expressed in joint swelling and pain.
If you happen to feel such symptoms while taking the supplement, it means you are allergic and should avoid glucosamine-based supplements.
The most common allergy is based on sea food allergy, as we mentioned earlier and these allergies are pretty much common.
Glucosamine intake is not recommended if you have a sensitive stomach or gastritis.
The highest daily intake, that is considered safe, non-toxic for the inner environment is up to 1500 mg.
It is also proven that intravascular glucosamine use may worsen insulin sensitivity; therefore, such use of it is not recommended for people suffering from diabetes.
Which Supplements Contain Glucosamine?
Glucosamine is found in three forms- Glucosamine hydrochloride, glucosamine sulfate and N-Acetyl-Glycosamine, as the last one is considered the least potent one.
The supplements containing this substance increase joint recovery and support the immune system.
Glucosamine containing supplements are either isolated glucosamine, or complexes with other substances like chondroitin- A substance with similar effect.
Complex supplements with more than one substance gain more and more popularity, as the main additions to glucosamine include Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, minerals and herbs that have anti-inflammatory properties.
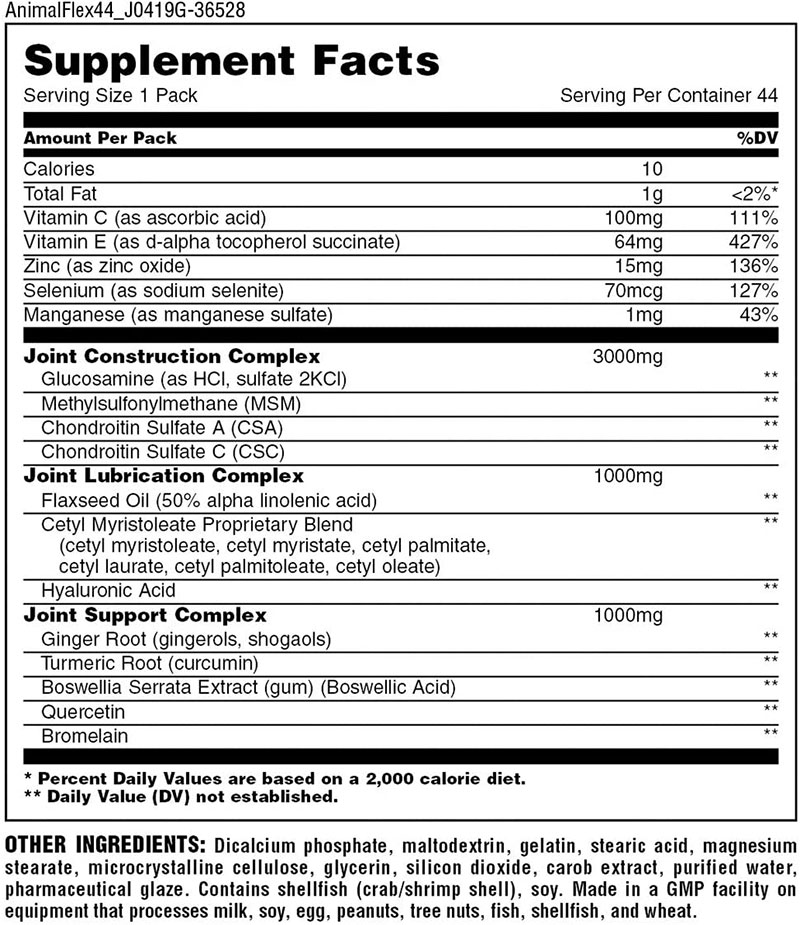
One of the most popular complex products is Animal flex, manufactured by Universal.
These supplements are most often in the form of tablets, as the glucosamine content ranges from 500 to 2000 mg.
However, as the manufacturing processes advance, different forms like powder and liquids can be found on the market.
Isolated glucosamine supplements are mostly under the names “Glucosamine HCL” and “Glucosamine sulfate” – Products with up to 1000 mg per capsule can be easily obtained from the supplement shop, or online. (Our recommended product is at the bottom of the page, do give it a shot!)
What Can Glucosamine Be Combined With?
To this point, scientific research proves the benefits of combining this supplement with other substances that have a similar effect.
One of the most popular combinations, as we mentioned earlier is glucosamine and chondroitin, as the synergistic effect of these two is proven.
Chondroitin itself adds up and enhances to the effect of glucosamine, as it regulates inflammations in the body.
Another popular substance, often combined with glucosamine is methylsulfonylmethane.
It is proven that this combination does not really suppress the inflammation and regulate pain, compared to isolated intake of one of them, however, this exact combination can regulate inflammations in the problematic zones and improve motor performance in patients suffering from arthritis.
In the long term, combining glucosamine with fish oil, demonstrates a significantly stronger effect, compared to isolated glucosamine intake.
To feel a significant difference however, it needs to be taken long term (At least 6 months)
One of the most successful synergistic combinations of glucosamine is the herb called boswellia serrata.
It is proven that 125 mg per kilogram of bodyweight of both substances, have the equivalent effect of 100 mg ibuprofen, when it comes to treating arthritis.
Often times however, glucosamine is wrongly interpreted as a natural substitute of non-steroid anti-inflammatory means.
It is worth noting that combining glucosamine and ibuprofen is shown to suppress pain stronger than isolated ibuprofen intake.
Therefore, we can conclude that in reality, glucosamine strengthens the effect of some anti-inflammatory medicaments.
Other Physiological Effects Of Glucosamine
- Glucosamine supports wound healing
- Slows down the loss of cover cartilage tissue on the joint surface.
- Using up to 3000 mg glucosamine daily decreases the biomarkers of collagen degradation
- Glucosamine is proven to help reduce pain and improve mobility in patients with kashin-beck disease, which is pathologically similar with osteoarthritis
- Reduces joint pain in patients with osteoarthritis
- Can be a building block for cartilage tissue
- Glucosamine is more effective if injected
Why Should You Take Glucosamine?
As the organism ages, the concentration of glucosamine in the body decreases, meaning that the demands of it grow overtime.
The most popular glucosamine compound is glucosamine-sulfate.
Usually, that is the exact substance, often included in supplement complexes.
Glucosamine is appropriate for any strength athletes that are looking to treat joint problems or prevent such.
Critics On Glucosamine
The world of science is yet unsure if this substance has the expected effect, claimed by orthopedists.
While some researches show that it really has no positive effect in patients with osteoarthritis, others confirm its pain-reducing and progression retardation properties, in such conditions.
Due to these uncertainties, we would highly advice you to test out this supplement, if, of course you really need it.
While using it, track any possible effects and determine whether or not it works for you.
From then on, glucosamine can be moderately dosed, and used on the regular basis.
Again, worth mentioning that this supplement should be taken with food, due to its stomach-irritating properties, and as everything else on this planet- Excessive levels of intake should not be reached.