Testosterone, often referred to as the “male hormone,” plays a crucial role in both men and women’s health. While it is true that men typically have higher levels of testosterone than women, this hormone offers a wide range of benefits that extend far beyond gender-specific traits. In this article, we will explore the multifaceted advantages of testosterone, its impact on physical and mental well-being, and the various ways in which individuals can maintain healthy testosterone levels.
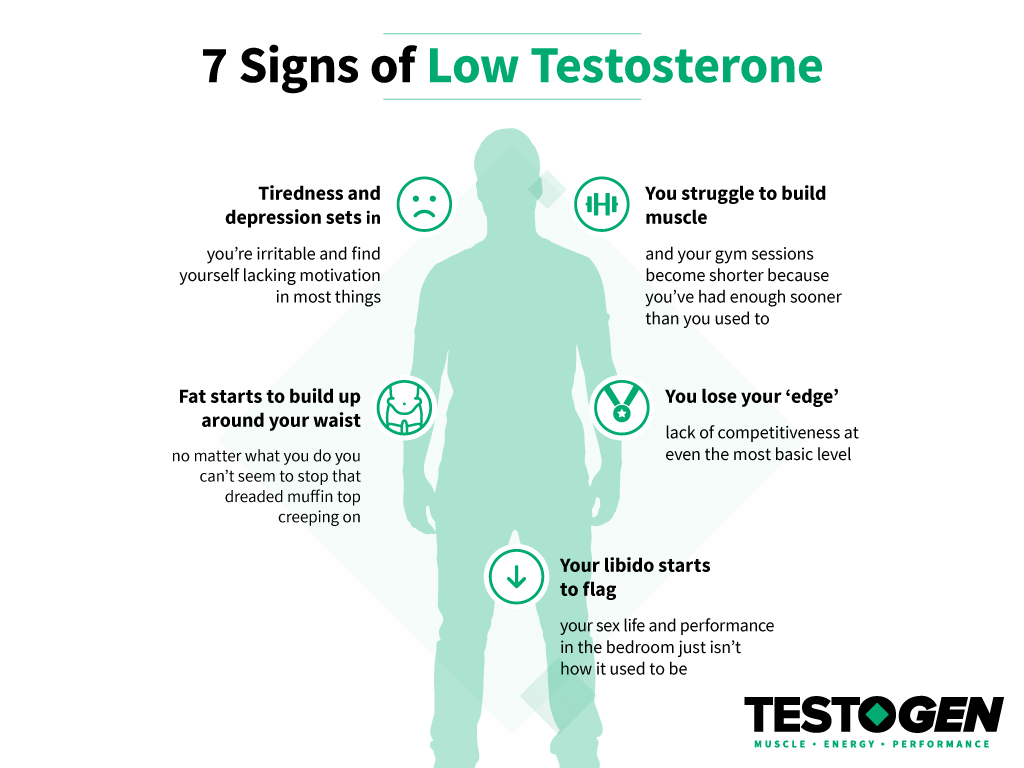
1. The Importance of Testosterone
Before delving into the foods that can potentially lower testosterone, it’s essential to understand why this hormone is so crucial for men’s health.
Testosterone is primarily produced in the testes and, to a lesser extent, in the adrenal glands. It serves numerous vital functions, including:
- Muscle and Bone Health: Testosterone plays a pivotal role in the development and maintenance of lean muscle mass and bone density.
- Libido and Sexual Function: It’s no secret that testosterone is linked to sexual desire and performance.
- Mood and Well-being: Adequate levels of testosterone contribute to an overall sense of well-being and mental health.
- Metabolism: Testosterone influences the body’s metabolism, affecting how it stores and burns fat.
- Cognitive Function: Some studies have suggested that testosterone may influence cognitive abilities.
Now that we understand the importance of testosterone, let’s examine how our diet can affect these critical functions.
2. The Food-Testosterone Connection

It’s common knowledge that diet significantly impacts our overall health, but its effect on hormones, including testosterone, is less frequently discussed. Several dietary factors can influence testosterone levels, either positively or negatively. In this section, we’ll focus on the foods that can potentially decrease testosterone production.
2.1 High Sugar Diets
Excessive sugar consumption, especially from sugary drinks and processed foods, can lead to a condition known as insulin resistance. This condition, characterized by the body’s reduced sensitivity to insulin, can indirectly affect testosterone levels. When insulin resistance occurs, the body compensates by producing more insulin, which can disrupt hormone balance and lead to lower testosterone levels.
To mitigate this risk, it’s advisable to reduce your intake of sugary foods and opt for a balanced diet with complex carbohydrates from sources like whole grains, vegetables, and fruits.
2.2 Processed Foods and Trans Fats
Processed foods, often high in trans fats, are a double-edged sword when it comes to testosterone levels. Trans fats are known for their detrimental effects on cardiovascular health, but they can also interfere with testosterone production. Research has shown that a diet rich in trans fats can lead to decreased testosterone levels, as well as a host of other health issues.
To protect your testosterone levels, limit your consumption of processed and fast foods, and instead, prioritize whole foods such as lean meats, fish, and vegetables.
How to boost your testosterone? Read our review on Testogen which is one of the best testosterone booster in the market!
2.3 High Alcohol Consumption
While moderate alcohol consumption may not significantly affect testosterone levels, excessive drinking can indeed lead to hormonal imbalances. Chronic alcohol abuse can damage the testes, the primary site of testosterone production, and disrupt the hormone’s regulation. Furthermore, excessive alcohol intake can result in higher estrogen levels in men, further diminishing testosterone’s impact.
It’s advisable to consume alcohol in moderation, if at all, to maintain healthy testosterone levels. If you choose to drink, do so responsibly and avoid binge drinking.
2.4 Soy-Based Products
Soy is a popular plant-based protein source and is widely used in various processed foods and meat substitutes. However, soy contains compounds called phytoestrogens, which mimic the effects of estrogen in the body. High levels of phytoestrogens can potentially interfere with the body’s natural hormone balance, including testosterone.
If you consume soy-based products regularly, consider moderating your intake, especially if you are concerned about testosterone levels. Opt for other plant-based protein sources like beans, lentils, and tofu in moderation.
2.5 Flaxseeds
Flaxseeds are renowned for their health benefits, including their high fiber and omega-3 fatty acid content. However, flaxseeds are also rich in lignans, which have been shown to possess estrogenic properties. While flaxseeds may have a favorable impact on women’s hormonal health, men should consume them with caution to avoid any potential interference with testosterone.
If you enjoy flaxseeds for their other health benefits, consider moderate consumption, and monitor how your body responds to them.
2.6 Mint and Spearmint
Mint and spearmint are widely enjoyed as herbal teas, breath fresheners, and culinary herbs. However, some studies suggest that excessive consumption of mint can have a negative impact on testosterone levels. These herbs contain compounds that may exert anti-androgenic effects, potentially decreasing testosterone.
If you’re an avid mint tea drinker, it may be a good idea to diversify your herbal tea options and enjoy mint in moderation.
3. Balancing Your Diet for Optimal Testosterone Levels

Now that we’ve explored the foods that might negatively affect testosterone, it’s equally important to discuss how you can optimize your diet to maintain or boost your testosterone levels.
3.1 Nutrient-Rich Foods
A balanced diet that includes an abundance of nutrient-rich foods is essential for hormonal health. Nutrients like vitamin D, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to support healthy testosterone levels. Foods that can contribute to these nutrients include:
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids.
- Lean Meats: Turkey, chicken, and lean cuts of beef provide essential proteins and zinc.
- Eggs: Eggs are a rich source of vitamin D and healthy fats.
3.2 Fiber and Vegetables
A diet high in fiber from vegetables and fruits can help with weight management and insulin sensitivity. These factors, in turn, positively influence testosterone levels. Aim to include a variety of colorful vegetables and fruits in your daily meals.
3.3 Healthy Fats
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are crucial for overall health and can support testosterone production. Avocado, olive oil, and nuts are excellent sources of these healthy fats.
3.4 Adequate Protein
Protein is essential for muscle growth and repair, both of which are linked to testosterone levels. Incorporate sources of lean protein such as chicken, turkey, and plant-based options like tofu and legumes into your diet.
3.5 Resistance Training
In addition to dietary changes, incorporating resistance training into your fitness routine can be highly effective in increasing testosterone levels. Weightlifting and strength training exercises are particularly beneficial for promoting muscle growth and boosting testosterone production.
3.6 Stress Reduction
Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which can have a negative impact on testosterone. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help balance hormones.
4. Lifestyle Choices and Their Influence on Testosterone

Beyond diet, several lifestyle choices can impact testosterone levels. Let’s explore some of these factors.
4.1 Sleep
Adequate and quality sleep is essential for maintaining healthy testosterone levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to allow your body to recover and regulate hormonal functions.
4.2 Weight Management
Being overweight or obese can lead to increased estrogen levels and lower testosterone. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can positively influence hormonal balance.
4.3 Stress and Mental Health
High-stress levels and mental health issues can contribute to hormonal imbalances. Engaging in stress-reduction activities, seeking support when needed, and maintaining a positive mental state are vital for overall health.
5. Conclusion
Your diet plays a substantial role in your overall health and, specifically, your testosterone levels. While some foods can potentially undermine testosterone production, a balanced diet rich in nutrient-dense foods can help maintain or boost your hormone levels. Furthermore, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management can further support your hormonal well-being.
Remember that individual responses to dietary changes can vary, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or endocrinologist, to address any concerns about your testosterone levels. Making informed dietary and lifestyle choices can help you maintain optimal testosterone levels and support your overall health and well-being.